
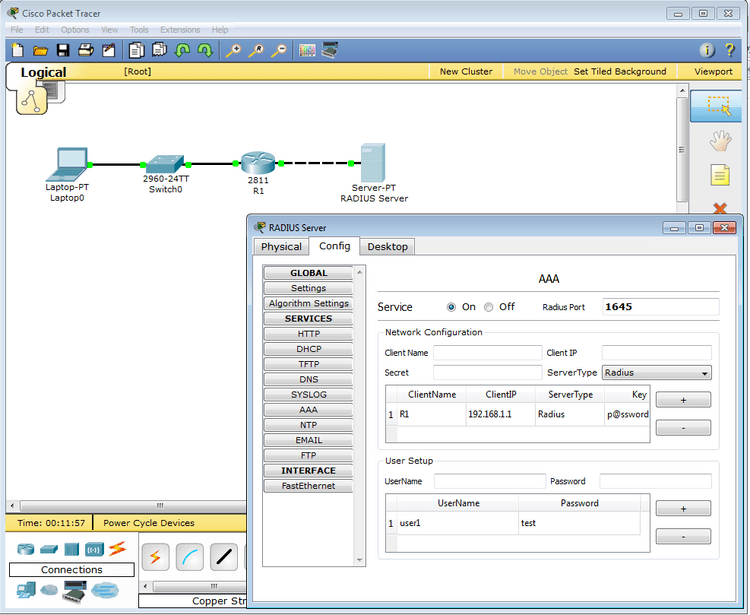
Item Protocolsĭescription LAN: Ethernet (including CSMA/CD*), 802.11 a/b/g/n wireless*, PPPOE Switching: VLANs, 802.1q, trunking, VTP, DTP, STP*, RSTP*, multilayer switching*, Etherchannel, LACP, PAgP, IP CEF TCP/IP: HTTP, HTTPS, DHCP, DHCPv6, Telnet, SSH, TFTP, DNS, TCP*, UDP, IPv4*, IPv6*, ICMP, ICMPv6, ARP, IPv6 ND, FTP, SMTP, POP3, VOIP(H.323) Routing: static, default, RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP, single-area OSPF, multi-area OSPF, BGP, inter-VLAN routing, redistribution Other: ACLs (standard, extended, and named), CDP, NAT (static, dynamic, inside/outside, and overload), NATv6, Netflow WAN: HDLC, SLARP, PPP*, and Frame Relay* Security: IPsec, GRE, ISAKMP, NTP, AAA, RADIUS, TACACS, SNMP, SSH, SYSLOG, CBAC, Zone-based policy firewall, IPS QoS: Layer 2 QoS, Layer 3 Diffserv QoS, FIFO Hardware queues, Priority Queuing, Custom Queuing, Weighted Fair Queuing, MQC, NBAR* * indicates substantial modeling limitations imposed Network topology creation Devices: generic, real, and modular with customizable images Routers, switches, hosts (Server, Desktop and Laptop), hubs, bridges, wireless access points, wireless routers, clouds, ASA, and DSL/cable modems Device interconnection through a variety of networking media Multiuser remote networks Hierarchy of device, wiring closet, building, city, and intercity views Structured cabling: create BendPoints and GroupPoints in cables and color code cables Ethernet cable length display and length limitation connectivity enforcement We invite you to use the help files and tutorials to learn about the major features of the program, which include the items in the following table. Packet Tracer was created to help address the Digital Divide in networking education, where many students and teachers lack access to equipment, bandwidth, and interactive modes of learning networking. Real computer networks, experienced both in-person/hands-on and remotely, remain the benchmark for understanding network behavior and developing networking skills. Like any simulation, Packet Tracer relies on a simplified model of networking devices and protocols. Packet Tracer supports student and instructor creation of simulations, visualizations, and animations of networking phenomena. Packet Tracer is an integrated simulation, visualization, collaboration, and assessment environment. Packet Tracer is a medium fidelity, network-capable, simulation-based learning environment for networking novices to design, configure, and troubleshoot computer networks at a CCNA-level of complexity. Introduction Welcome to Cisco Packet Tracer. Important notes or tips are presented in tip boxes like the following: If you are a first-time user, please read the help files in order. Annotated screenshots are used to aid your understanding. Although the help files may be used as a reference guide, the pages are meant to be read in order (especially the sections presented at the beginning). Using the Help Files The help files are designed to familiarize users with the Cisco Packet Tracer interface, functions, and features.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
